
Cornea / Keratoconus
Cornea: Cornea is the outer most of the eye. Cornea contributes towards around 70 percent of the focussing power of the eye. Refractive problems like myopia, hyperopia and astigmatism are caused due to a change in shape of the cornea.
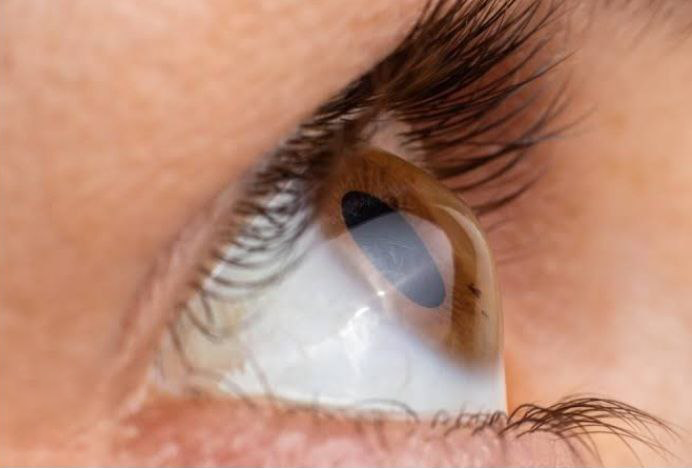
Keratoconus: Keratoconus is a progressive disease of the eye in which the cornea becomes thin and begins to bulge into a conical shape. This results in irregular refraction of light rays entering the eye, resulting in blurred, distorted vision and a high astigmatic error (high cylindrical power of glasses).
It usually affects both eyes, although only one eye may be affected initially. This usually starts at the time of puberty and progresses in young people. Progression slows down after the age of 40 years.

Investigations
Keratometery
Corneal topography
Anterior Segment Optical Coherence Tomography (ASOCT)
Ultrasonic Pachymetery
Treatment
Halting the progress of Keratoconus
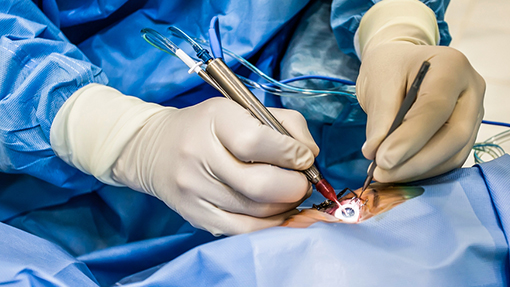
Corneal collagen cross linking is useful in halting the progression of the disease. This is also known as C3R or CXL.
C3R or CXL is highly successful treatment procedure in which your surgeon uses riboflavin drops and exposes the eye to controlled ultraviolet radiation which makes the cornea stronger and helps flatten it.
There are various techniques of CXL depending on the patient’s corneal thickness. In corneal thickness > 400micron standard epioff technique with isotonic riboflavin is performed using accelerated CXL.
In thinner corneas, use of hypo-osmolar riboflavin, contact lens assisted CXL, Stromal lenticule assisted CXL, or customized thin cornea protocols.
Rehabilitation of vision after halting the progress of Keratoconus
For visual rehabilitation, spectacles are useful in mild keratoconus.
Contact lenses mask the irregular corneal surface and improve vision.
Rigid gas permeable (RGP) lenses, hybrid lenses, scleral lenses give promising results in keratoconus.
Surgical intervention
INTACS, Corneal Inserts or Intracorneal Ring Segments: In patients who are intolerable to contact lenses can opt for intrastromal corneal ring segments (INTACS)
INTACS procedure does not prevent progression, however, this could help to regularize corneal surface to correct visual acuity.
T-CAT, Topography-guided Custom Ablation Treatment: It could be used in the management of keratoconus to modify corneal anatomy using excimer laser. This procedure could be combined with various CXL protocols.
ICL: After CXL or C3R, when refraction stabilises, ICL is put inside the eye to make patients spectacle free.
Keratoplasty (corneal transplantation): In advanced keratoconus with progressive thinning of cornea, eye surgeon prefer to replace the cornea with donated cornea, this surgery is called Keratoplasty.
